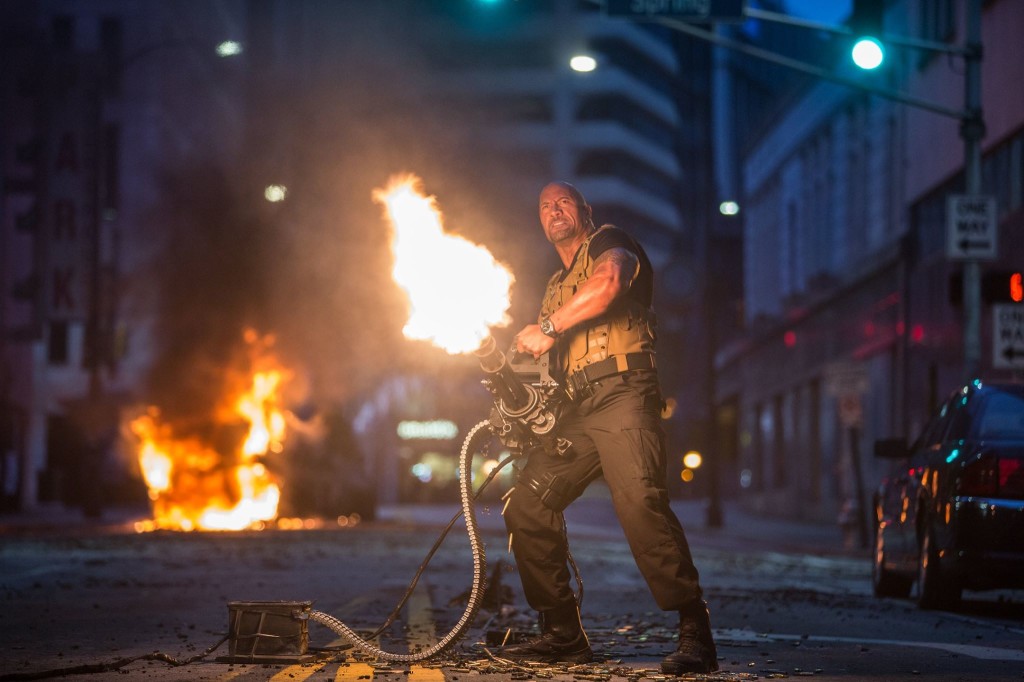Genre: TV Pilot – Thriller
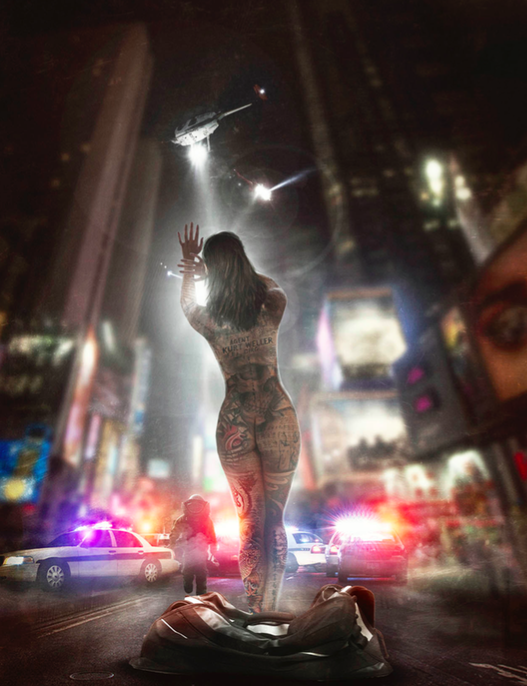
Premise: When a naked woman shows up in the middle of Times Square covered head-to-toe in tattoos, a special FBI unit realizes that the tattoos are some kind of treasure hunt… but for what?
About: Let’s be honest. Nobody’s really pining for the next NBC show. The Peacock’s been trying to play cards at the cool kids table for a couple decades now and failing miserably. I’ve seen mom jeans with more swag. But I think they’re finally realizing that if they don’t change, their feathers will wither and die. The Big 3 networks are being squeezed out slowly enough that they don’t quite realize it, and it’s the young guys with no power inside these companies who are screaming: ACT NOW! A cool show at least gives you some leverage, and Blindside is a show they’re putting a lot of hope into. Not only did it snag THE hottest actor that EVERY network in town wanted for their show in Sullivan Stapleton, but it had the coolest poster title page I’ve seen in a year reading scripts. Blindspot is a JJ Abrams 7 course mystery box feast. And that is both its biggest strength, and most crippling weakness. Creator Martin Gero has written for the HBO show, Bored to Death, as well as for BOTH Stargate shows.
Writer: Martin Gero
Details: 4th draft (Jan 18, 2015) – 61 pages
Pilots are funny. You have to give us something so captivating that we’ll want to come back for episode 2. But you don’t want to give us something so big that there’s no way episode 2 (and 3, and 4) can match it. Who wants to go Coney Island after you’ve been to Disney World? After reading Blindspot, I’m wondering how it’s going to make every ride Magic Mountain.
I mean, we have a scene where a subway train must race to avoid an underground tsunami. And we also have a man who’s trying to blow up the Statue of Liberty. What’s episode 2 going to be about? Preventing the space station from falling out of orbit? Episode 3? Going back in time to kill Hitler?
Blindspot is a ride and a half. But something tells me it’s unleashing a hurricane so strong, it has no choice but to run out of steam by the time it hits land. It’s the kind of experiment that’s worth taking though in this ultra-competitive market. If you’re going to set the bar, you might as well set it high.
Blindspot starts out with an immediately arresting image. A naked woman emerges from a bag in the middle of Times Square covered in tattoos with no memory of who she is. One of those tattoos reads simply: “Kurt Weller – FBI.”
Cut to Kurt Weller, a member of FBI’s CIRG unit (Critical Incident Response Group). No idea how this group’s different from every other FBI unit, but that’s not important when you see Weller being a BADASS and taking down an Ariel Castro type before he can kill the four women he’s been holding hostage in his house for a decade.
Weller’s notified afterwards of our mysterious Jane Doe and her artistic rendering of his name on her back. They do some tests on the poor girl but she can’t remember a thing. It’s Weller who realizes that her tattoos are some kind of treasure map. He keys in on one that leads them to an address where a Chinese man lives.
It’s here where Jane first learns she speaks Chinese, and, oh yeah, CAN F*&%ING TAKE PEOPLE DOWN WITH THE FORCE OF RHONDA ROUSEY. Clearly, Jane’s had training. But from who? From where?
A clue at the house leads them to Cho who they quickly learn is on the run. A video he’s left on his laptop indicates that he’s going to destroy the Statue of Liberty. Weller and Jane rush to stop him and as they get closer, it’s less clear who’s conducting the train. Is it Weller? Or is it Jane?
I don’t think it’s a spoiler to say they prevent Lady Liberty from being destroyed, but it’s afterwards when the real fireworks fly. Maybe, just maybe, Mysterious Jane is Weller’s long-lost sister. And maybe, just maybe, she was a co-conspirator in this little amnesia party. But why? What is it, exactly, that Jane plans to do once she regains her memory?
Somewhere, between approving a digital X-Wing shot and adding a deeper Chewbacca roar, JJ Abrams is smiling. If there’s a pilot that celebrates Abrams’ mystery box method more than Blindspot, I haven’t read it. Jane Doe is a mystery. Jane Doe’s tattoos set up a mystery. Weller’s sister disappearing when he was young is a mystery. Our Chinese man on the run is a mystery.
But as a wise writer once told me. “Yeah sure, you can mystery box your script to death. But at a certain point, if that’s all there is, people will get bored.” Indeed, I think Blindspot falls a little too much in love with its own mysteries, and ignores some of that emotion you need in order to connect with the audience. Which is what we were just talking about yesterday with Furious 7.
It’s funny because a couple of weeks ago I reviewed AMC’s “Badlands,” and complained how although it set up a lot of intriguing relationships, it lacked the multiple mystery boxes required to pique our curiosity for future episodes. Blindspot does the opposite. It gives us all the mystery boxes we could ask for, but doesn’t do anything on the relationship front.
If you’re forced to choose between these two, I’d much rather you focus too heavily on relationships than mystery boxes. That’s because TV, more so than film, is CHARACTER DRIVEN. We have to see a future with the characters, since we plan on being with them for years. Mystery boxes are a lot like heroin. Their emergence gives us this big initial high, but that high dies out quickly. And then what do we have left? Character exporation, whether it be between characters or within the characters, reaches the audience on a much deeper (and more lasting) level.
That’s why I loved Lost so much. Sure that show was Mystery Box Theater, but you can’t deny how intensely it explored its characters. It devoted half of every episode to flashbacks specifically so we could explore the characters. That may be the biggest lesson here. If you can write a pilot that pulls off the mystery boxes AND character exploration, you’ve probably got yourself a winner.
I’m torn on what to rate Blindside. Despite its shortcomings, it moves breathtakingly fast. I may not know these characters as well as I wanted to after the read, but how many 60 page scripts can be read in 30 minutes? And not just because the writing is sparse – but because the plot is so well-paced.
And it’s FUN! We can’t dismiss the fun-factor after seeing the way Furious 7 dominated the weekend. The average person isn’t like you and me, nitpicking every little issue in a story. They’re people who like to unwind and watch something entertaining. Blindspot is definitely that. So for that reason alone, you should probably check it out.
[ ] what the hell did I just read?
[ ] wasn’t for me
[x] worth the read
[ ] impressive
[ ] genius
What I learned: If a script is very strong in one area, chances are it’s weak in another. Identify that weak spot and address it. Blindspot’s strength is that it moves exceptionally fast. It’s an extremely well-paced script. But a big reason for that is that there’s no character exploration. The script’s fast cause it doesn’t have any of those slower scenes that explore character conflicts or character problems. You need those in a script (especially a TV script).
Genre: Action
Premise: A group of hot-shot car enthusiasts help a secret government black ops group take down a terrorist, all while avoiding the vengeful brother of a man they put in the hospital.
About: This is the latest installment of The Fast & The Furious phenomenon, and easily the most talked about. That’s because one of its key actors, Paul Walker, died, ironically, in an unrelated car accident during shooting. They had to stop production for a few months to rewrite the script, since they only shot half of Walker’s scenes. They eventually brought in Walker’s lookalike brothers to finish the film, and went to Peter Jackson’s WETA digital effects company to do some cut and paste jobs with Walker’s face. The film came out this weekend and was the first to make 9 gablillion dollars at the box office.
Writer: Chris Morgan
Details: 137 minutes
So let me see if I got this right. Michelle Rodriquez has amnesia and can’t remember she’s married to Vin Diesel. A guy named Deckard Shaw, who’s part of a double secret probation London Black Ops organization, destroys a hospital because he’s mad that they’re not giving his patient brother enough attention. He then leaves his brother in said burning hospital to go fight the people who hurt his brother in the first place.
There’s an international terrorist named Mose Jakanda who’s kidnapped a hacker who’s created something called the “eye in the sky” which can find anybody in the world within two hours. Snake Plissken, who’s now an army general for an American Black Ops team that specializes in having really expensive cars around, promises to help Vin Diesel get Deckard Shaw before Shaw gets him if he’ll go reverse-kidnap the hacker who created the eye in the sky.
The thing is, this new terrorist only travels on roads that are inaccessible to cars (huh?) so Vin’s crew has to parachute the cars onto the road via plane only. After Vin steals the hacker back from the terrorist, Deckard Shaw shows up to try to kill Vin, despite not having access to a plane that parachutes cars out of it. Vin survives, and somewhere around this point I realize that I’ve never seen Furious 6 even though I was absolutely positive I had.
For reasons that never become clear, Mose Jakanda teams up with another American Black Ops unit that has access to predator drones and uses one of these drones to stalk Vin and his buddies in Los Angeles. In the meantime, Deckard Shaw, who it’s still not clear if he’s working with Jakanda or just always shows up when he’s around, also attends this Los Angeles showdown, where he corners Vin on the top of a parking garage and fights him with crowbars, all while Tyrese yells a series of phrases through an unknown radio channel that all basically amount to, “Oh hell no! That shit did not just happen!”
To try and hold Furious 7 up to the standards of proper screenplays is kind of like trying to hold the McDonald’s drive-thru guy who needs you to repeat your order three times up to a Michelin chef. It’s not really fair.
And that’s a problem. Young screenwriters who want to write cool action movies are going to see this and think it’s what you need to write to sell an action spec. It’s not. Furious 7 is a series of set-pieces held together by threads so loose, they feel like an autistic child trying to socialize at a birthday party.
There’s a desperation as characters try to explain what they’re doing, and despite the writer’s best attempts to distract us from this reality (distractions that are almost always Tyrese yelling something like, “Oh hell no! This shit is WHACK!”), it’s clear that unless action is involved, Furious 7 is like a hipster at a biker bar.
So I’m watching all this go down and wondering, like many in Hollywood, what makes these films so successful. They started out doing solid numbers, but the third installment was a B movie and made 27 dollars at the box office. Episodes 4-7, though, became box office titans, competing with the most powerful comic book properties for yearly domination.
You might say, “Well yeah, it’s got hot women and fast cars. Of course it’s going to do well.” Ehh, but so did Need for Speed. Why didn’t that film do Furious numbers? Or you might say, “Duh, it’s because of Vin Diesel.” The problem with that theory is that Diesel isn’t exactly tearing it up at the box office outside of the Furious films.
And then, as I was watching this film, it came to me like a ray of light shining through a lone hole in the clouds. It’s no secret that the franchise plays extremely well to Latinos (they make up the highest audience for the films at 37%). What do Latinos value over everything else? Family. Family is extremely important to the Latino culture. What are the Fast and Furious films about? You got it. Family. The Fast and Furious group considers themselves a family. The characters are getting married and creating families. Vin’s sister is married to Paul Walker. Paul Walker’s character now has a child. The Rock reveals he has a kid in the movie. The word “family” is uttered somewhere in the neighborhood of 732 times (Vin Diesel to Shaw: “I don’t got friends. I got family.”).
There’s no doubt that fast cars and hot women are going to bring in moviegoers. But for a film to become a phenomenon, there’s got to be something more to it. You got to find a way to connect with the audience on another level. Here, that level is emotion. It’s the importance of family that makes this franchise more than a bunch of car chases.
And this is actually good news for writers. For everyone who thinks you have to sell your soul to break into Hollywood – this proves that audiences want to connect on a deeper level with their movies. Do I think Furious 7 rivals the emotional intensity of, say, The Imitation Game? No. But the fans of this series obviously do.
Now before you go off to write Terms of Endearment with cars, let’s back up to the make-or-break component of any action script – the set pieces. The key to writing a saleable action spec is to write set pieces that haven’t been seen before. So here we have cars jumping out of planes. We have cars jumping from skyscraper to skyscraper. These were things we hadn’t seen before. They were stupid fun – sure – but they were original stupid fun.
If you’re going to accomplish anything in your action script, make sure it’s to give us UNIQUE SET PIECES. If I read a set-piece in a script that I’ve already seen before, I’m done with that script. Just like in a horror script, you have to give us unique scares. Just like in a thriller script, you have to give us unique thrills. In an action script, the one job you gotta get right is to write unique action.
Speaking of action, I want to finish with a warning to all future action writers out there. Beware of writing huge crews into your action scripts. As convoluted as the plotting here was, I have to give it to Chris Morgan for juggling all these characters. In each action scene, he was usually cutting between a dozen different characters. For any of you who’ve had to write scenes like this, you know how difficult it is to keep track of that many people.
Usually, you only have one or two featured segments in an action scene. But if you have 12 characters, you now have to keep the audience abreast of where they all are. You can’t just focus on the Vin Diesel part for the whole 10 minutes and then show Michelle Rodriquez at the very end or everyone will go, “Where the hell was she the whole time?” This forces you to come with things for everyone to do. And the more people you’re cutting between, the harder to follow everything is.
If you have a clear goal (get the hacker from the bus) a set piece can survive this complexity. But if the goal is even mildly unclear (as is the case with Furious 7’s climax – why the hell was a terrorist coming to Los Angeles again????), cutting between that many people can destroy the sequence. It’s yet another reason to celebrate movies like Star Wars. They make it so damn clear what the ending goal is that the set piece can survive any level of complexity.
Now you might think with all this criticism that I hated Furious 7. Actually, that’s not true. As sketchy as the screenwriting is here, the action is borderline amazing. Like I said before – we see things in this movie that we’ve never seen before. And this installment of the franchise seems to be more reliant on real stunts than the others, making for a much more realistic experience. I mean they really did drop cars out of planes for that plane drop sequence. I’m not sending any aspiring screenwriters to the theater to study Furious 7’s script. But if you want to enjoy the hell out of some amazing action, there are worse ways to spend your evening.
[ ] what the hell did I just watch?
[ ] wasn’t for me
[x] worth the price of admission
[ ] impressive
[ ] genius
What I learned: Figure out who you’re targeting and write what matters to that group into your screenplay. The writers and producers of Furious 7 realized they were targeting the Latino audience here, so they focused the story on family. A few years ago, The Blindside knew it was targeting Christians, so it infused a lot of Christian values into the script. Know who you’re writing to and then give that group what they relate to.
NOTE: THE SCRIPTSHADOW NEWSLETTER HAS BEEN SENT! CHECK YOUR SPAM AND PROMOTIONS FOLDERS IF YOU DIDN’T RECEIVE!

It’s a delicious screenwriting Saturday. Not only are you getting today’s offerings, and not only are you getting your daily reminder to enter the Scriptshadow 250, but later tonight, the Scriptshadow Newsletter will be hitting your mailboxes. Yaaaaay!!! And I’ll be reviewing a certain high-profile screenplay that is guaranteed to become one of the biggest movies ever. So make sure to check your SPAM and PROMOTIONS folders later tonight. And if you’re not yet signed up to receive the newsletter, you can do so here!
Title: Miss Universe
Genre: Sci-Fi Comedy
Logline: A vapid beauty queen is abducted by aliens who think her title means she’s Earth’s ambassador to the universe.
Why You Should Read: It’s “Galaxy Quest” meets “Legally Blonde.” Deep space has never been more shallow (Carson note: When everyone pitched their ideas on “pitch your script day,” this idea shot to the top of the list!)
Title: Time to Forget
Genre: Action/Thriller
Logline: A CIA agent whose memory has been erased is given four hours to assassinate the President of Palestine, but when he starts to doubt the validity of his mission, he finds himself hunted by authorities and mercenaries alike as he races to discover his true identity.
Why You Should Read: In the past Carson has written that theme and message are what tie a story together. In that sense, I’ve tried to knit this script up as tightly as possible. Rather than use amnesia as just a standard identity quest, I wanted to pose the question, “at what point does holding on to the past become damaging, and what is the cost of letting go?” In ways both direct and subtle, every major character is an expression of that theme. — Why else should you read? It’s also an action filled, GSU-loaded, race against the clock thriller that doesn’t get bogged down by its message or forget to have fun. Hopefully the SS community enjoys reading it as much as I enjoyed writing it.
Title: Street Sharks
Genre: Family / Sci-Fi / Action-Adventure
Logline: A timid college student and his three brothers search for their missing father until they are kidnapped by a technology mogul and mutated into superhuman sharks.
Why you should read: My partner and I are both college graduates looking to get into the screenwriting industry. We wrote this script intending to pitch it to the industry, but as this is our first screenplay we do not have enough of a reputation to acquire the film rights to the Street Sharks franchise. We realize there’s no point in letting the script sit around, so we would like to receive feedback from you and the community on our writing. I hope everyone has as much fun reading it as we had writing it!
Title: Rose
Genre: Drama
Logline: After a rebellious slave falls in love with her master’s step-son, the two attempt to run away together before she can be sold to a villainous new owner.
Why you should read: I started out as an actor, and got into writing around ’08. I have two produced screenwriting credits (but don’t let those fool you, I wait tables). Most of my work, to date, has been comedic. This script is not. I read Uncle Tom’s Cabin in 2011 and a story with a female lead popped into my head. I was compelled to write it. People around me were like: what…? A story about slavery? You’re crazy, Brooks. But, I wrote it. I know it’s a Sisyphean task to get it produced but perhaps it can do well in competition. SS had been like a second film school for me. A great place to improve your script. So I submit it here to the Scriptshadow faithful today.
Title: Valentino’s
Genre: Thriller
Logline: In a quiet New Jersey town, a struggling Italian family discovers bags of stolen mob money buried in the basement of their restaurant – and someone is coming to collect.
Why you should read: You reviewed this a few years ago for me. A first draft actually. You seemed to like it and I really liked the notes you had to give. I spent a few months on rewrites, submitted to the Blacklist where it did well with an 8. That reviewer really liked it as well. Ok. Great. Heard nada. Then this went into Warners last year and they passed. I’d never just give up because one studio passed. Hell no. But now what? — I’ve always loved this story and am ready to give this another look now that some time has passed. It seems to get somewhere then go nowhere. What is missing from this story to push it above par?
Get Your Script Reviewed On Scriptshadow!: To submit your script for an Amateur Review, send in a PDF of your script, along with the title, genre, logline, and finally, something interesting about yourself and/or your script that you’d like us to post along with the script if reviewed. Use my submission address please: Carsonreeves3@gmail.com. Remember that your script will be posted. If you’re nervous about the effects of a bad review, feel free to use an alias name and/or title. It’s a good idea to resubmit every couple of weeks so your submission stays near the top.
Genre (from writer): Action/Adventure
Premise (from writer): Back-stabbed by his employer and marooned in Mexico, a tough, drug-running pilot struggles to fly himself and the family that rescued him back to America alive.
Why You Should Read (from writer): Growing up on the border, there are lots of crazy stories you hear about trafficking (mostly from your friends that are doing it). With this story I wanted to take a lot of that raw material and structure it with an action adventure spin and a solid protagonist while still having some of the authenticity of experience. It was a trickier line to walk than I imagined, but I’ve gotten a lot of positive feedback about the script so far so something must be working. I’m excited to see what the SS readership thinks (and if they think I pulled off the balancing act) and I’m pumped to use any and all feedback to keep improving the writing!
Writer: Jeffrey Doka
Details: 109 pages
Today’s script comes from a former reader so I’m not surprised at all that it won Amateur Offerings. When you read a lot of scripts, you get a feel for the rhythm of a screenplay. With writers who don’t read, I often notice their scripts move slower. They don’t know what it’s like to read five scripts in a row where nothing happens for 30 pages, so they make the same mistake themselves.
I’ve also given notes to Jeff on this script, although sadly those notes haven’t been applied yet. If I remember correctly, I thought more could’ve been done on the character front and that the ending was messy. I’m also wondering if The Runner satisfies the “larger than life” rule I talked about yesterday in my concept post. Does this concept feel big enough to be a movie? I’d like to hear your thoughts on that in the comments.
32 year old single-living Rich Davison is a drug runner. He flies Cessnas so packed with weed, the exhaust gets you high. His life seems to be going great until his latest shipment is revealed to be a scam. Inside the weed-bins is cold hard white powder. That may not seem like a bad thing. Drugs are drugs, right? Nosiree. If Rich were to get caught with cocaine instead of weed, he’d be in prison for life.
So Rich lets his employer, Juan Montero, have it, and to Montero’s credit, he apologizes for his “calculated risk.” But Rich is done. He’s ready to go off to a beach somewhere and drink Long Islands all day.
Not so fast, says Montero. You still have one job left before I let you go. Rich begrudgingly accepts, but on his subsequent flight into Mexico, he finds that his plane’s been rigged with a bomb (courtesy of you-guessed-it). He grabs a parachute and leaps out just in time, drifting into Mexican territory, territory it just so happens Montero runs.
A beautiful young woman, Elena Santiago, saves Rich and brings her to her small farming home, where she lives with her father and daughter. As she nurses Rich back to health, he plots his escape via a nearby airfield. But it turns out everybody’s got an angle here. Elena only rescued him so that he could fly her and her family to America, away from the oppressive Montero.
Soon Montero, who’s been searching for his former employee, descends upon the town, where he knows someone is hiding Rich. With both his and Elena’s family’s lives on the line, Rich orchestrates a daring escape amongst Montero’s ruthless gang. But nothing about the escape goes as planned.
Reading this again, I realize that Jeff and I see this film a little differently. I see this as a potential version of the Harrison Ford film, The Witness. A selfish thrill-seeker used to a fast and furious lifestyle is forced to live in a simplistic Mexican farming town while he heels. At first he’s resistant to the lifestyle but as time goes on, he starts to understand and appreciate the people and their way of life.
It works ironically as well. The script is called “The Runner” and yet our “runner” is forced to stay still in this community for the whole movie. He gradually, then, connects with the family, and as soon as he’s healed decides to save both himself and them.
The way the script is now, Elena is basically holding Rich hostage under the agreement that he has to fly her and her family (and friends) out of here. I don’t think that’s the way to go. I think Elena should be happy with her life here. Rich, in the meantime, is all about himself. He’s trying to heal as soon as possible in order to get the hell out.
Meanwhile, Montero (who wouldn’t be associated with this community in the new draft) has been slowly putting together the clues of this crashed plane, getting closer and closer to where Rich is located. When he finally gets to the town, Rich realizes that even if he escapes, Montero will find out Elena housed him, and he’ll kill her family. So for the first time, Rich must think of someone other than himself. He has to orchestrate an escape for all of them, which is way more complicated than the escape he planned (stakes have been raised!).
The script then, becomes more of a character piece. The second act begins with his resistance towards these people and their way of life, and as time goes on, he makes a connection with Elena and her daughter, and starts to understand this world, and even appreciate it. I mean, it’s basically Witness, which was a great film and they haven’t really made anything like it since. So its structure is ripe for the picking.
I stress that angle because my biggest issue with The Runner was I never FELT anything. I wasn’t connected to these characters enough. And I think that’s because the second act is focused more on the escape than it is the conflict between the family and Rich. And remember my article from a couple of weeks ago. That’s where you want to focus your second act. Create a series of unresolved relationships and use the middle act to resolve them.
But yeah, Jeff is a good writer. I would recommend him to others. I don’t think this version of the script is where it needs to be yet, but I’m betting once he integrates both yours and my feedback, it’s going to be really good.
Script link: The Runner
[ ] what the hell did I just read?
[x] wasn’t for me
[ ] worth the read
[ ] impressive
[ ] genius
What I learned: You hear me talk about it all the time – way too much in fact. But as long as writers keep making the mistake, I’m going to keep bringing it up. WHEN IN DOUBT, KEEP IT SIMPLE. Writers think they need to make things really complex to be good, but you don’t. Usually, the simplest option is the best. Something I brought up to Jeff in the notes was his ending. The whole movie has been building up towards this plane escape. So what happens when it finally comes? Well, Rich escapes in the plane, goes to America, ends up coming back to save more people, is forced to take Montero back to America instead, and then, once in America, we take off one MORE time before “the end.” That’s three separate flights! It’s way too complicated. You have to structure this ending so that getting to the plane and leaving is it. Once they get up into the sky, that’s the movie. Casablanca doesn’t have Ilsa and Laszlo leave, come back, leave again, land somewhere, and then leave again. Just keep it simple!
Note: FOUR MONTHS LEFT UNTIL THE SCRIPTSHADOW 250 DEADLINE!!!
So over the past few weeks, I’ve had some discussions with writers gearing up to write their next screenplay. Some of these were new writers with only a few screenplays under their belt. Others have been trying to break in for 10+ years. The discussions universally gravitated towards, what’s wrong? Why haven’t my screenplays sold or gotten me an agent, or even gotten my best friend to read them?
95% of the time it comes down to that the concept isn’t any good. And the fascinating thing I’ve found over time is that the writer actually knows this. They’ll actually say to me, “I know that the concept isn’t very good but this isn’t about the concept. This is about the characters and their journey they go through and blah blah blah…”
Hold up, hold up, wait a minute, hold on.
What did you just say?
Did you really just say you knew the concept wasn’t any good? And you still wrote the script?? Believe it or not, this answer is so pervasive in the amateur writing ranks, that I don’t know why it still surprises me. The only explanation I can come up with for why they do it is that they believe they’re different in some way. That they’re special. And the rules don’t apply to them.
Unfortunately, that’s not how this business works. This business IS a concept-driven business. Not only because the script has no chance of getting made unless the concept is good. But because Hollywood is a numbers game. Everyone says no to everything – EVEN GOOD CONCEPTS. A yes only comes along every once in awhile. Therefore, you have to spread the widest net and get the most reads in order to get that yes. If you have a lame (or boring, or uninspired) concept, you’re not going to get the number of reads necessary for the odds to pay off. A good concept gets 50, 100, 200 times the number of reads a boring concept does. Imagine how much better your chances are of breaking in with those kinds of odds.
So how can we ensure we have a good concept? Aren’t those hard to come up with? I mean, if it were easy, everyone would be doing it, right? Well, before we get to how to write a good concept, let’s start with how to avoid writing a bad one.
A new phrase I want you to add to your screenwriting vocabulary is: “The Potential of Boring.” If your idea sounds like it has the potential to be boring, don’t write it. This is not to be confused with the script itself. The script (or the movie) may in fact be the greatest movie ever. But if it SOUNDS like it has the potential to be boring, don’t write it. Because, chances are, nobody’s going to read it. One of my favorite movies of the last two years is Philomena. I loved it. I would never, in a million years, however, allow an amateur writer to write that spec. Why? Because it’s about an old woman who goes searching for her son. The average person hears that and they think, “That has a strong potential to be boring.” Ideas that sound like they have the potential to be boring will not get read.
Another good way to know if you’ve got a boring concept is to play the elevator game. Pretend you’re stuck in an elevator with a Hollywood producer and he asks you to pitch your movie. Go, do it right now. Pitch your movie to Imaginary Producer in Elevator Guy. It should become clear very quickly whether you have a good concept on your hands. If you’re sitting there going, “… and she goes on this road trip of self-discovery and meets this guy. And he’s a drug-addict and then she remembers that what really brought her happiness was her poetry so she starts writing poetry, going from town to town, performing on the street…” That script’s not going to get read. “A young family excited to start their life together finds the perfect home, only for the college’s biggest fraternity to move in next door.” That’s going to get you a read.
As far as how to come up with a good concept, there isn’t any one way. There are clever ideas (like Neighbors, which I just noted), there are ironic ideas (like The King’s Speech, about a man who can’t speak who must give the most important speech in history), but if you’re still stuck trying to find that big idea, start by thinking “LARGER THAN LIFE.” Focus on a scenario that’s bigger than what happens in your everyday life. Going to pick up groceries then coming home to have a fight with your wife isn’t a movie idea. Going to pick up groceries, coming home to find your wife spread out on the floor dead, and the cops think you did it so you have to go on the run. That’s a movie idea. But I’m going to take this one step further. The larger than life your idea is, the more likely it is that it’s a movie idea. The Hunger Games, Guardians of the Galaxy, Captain America, The Hobbit, Transformers, Maleficent, X-Men, Big Hero 6. These ideas take place in different worlds, different universes in some cases. They’re larger than everything.
Let’s see how this can be applied to a basic idea. Say you want to write a movie about sex. So you write about normal people obsessed with sex. The movie is called Nymphomaniac. It makes 10 dollars at the box office. Why? Because there’s no “larger than life” angle to it. In comes Fifty Shades of Grey, currently the highest grossing movie of the year. Let’s now make one of the characters a billionaire. How many billionaires do you know in your everyday life? I’m guessing none. This aspect gives it a “larger than life” feel.
That might not be the best example, you can always skew the numbers in your favor when making these arguments, and there will always be exceptions to the rule. But I’m telling you. By and far, over the last 30 years of this business, this is the formula that wins out for writers trying to break into the industry.
Now there’s one writer I was talking to in particular who had been writing for about seven years. He was a good writer too, and he was frustrated that he still hadn’t broken in. I pointed out to him that none of his scripts really satisfied the “larger than life” criteria. There were a few you could argue were close. But like I said, the MORE larger than life it is, the better your chances are. And he tended to keep his stories more grounded, more based in reality. Which is exactly what he said to me. “But Carson, what if I just don’t like to write those kinds of movies?”
And I realized that some people just want to write about real human conflict, real human drama, without all the hoopla of a flashy concept. They’re more interested in reality. To these people I would start off by saying, “Understand that by taking that stance, you’re making your chances of success infinitely harder.” Once you’ve accepted that, we can go to the next piece of advice. And the next piece of advice would be this: “Stop bullshitting yourself.” It is completely possible to write a human drama wrapped inside a big concept. I’ll give you an example.
A couple of years ago, a writer broke through with one of the hottest scripts in town. It was called “Maggie,” and it was about a young girl who was turning into a zombie. Except in this take on the mythology, it took six months to turn into a zombie. I thought the script was okay, but that’s not the point. The writer was a genius. He wanted to write a story about cancer. But if he wrote a story about cancer, he knew no one would read it (keep in mind, this was before Fault in our Stars). So he placed the allegory inside of a marketable genre that made the story more high-concept. He told it as a zombie tale. And just like that, the concept is larger than life.
You can explore the human condition inside of ANY idea. So don’t fool yourself into thinking you have to write about a small town family who struggles to make ends meet after the dad loses his job in order to explore people. There was a script on the Black List a couple of years ago that did a wonderful job exploring a family amidst an alien invasion. Guess which one of those scripts is getting read? And they’re both doing the same thing – exploring the human condition. It’s just that one writer was smarter – he gave his story a wrapper that would make people interested. Hopefully, you can learn from him.